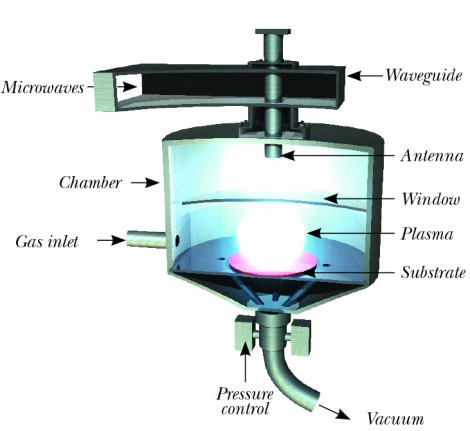
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a newer method of producing diamonds and is particularly valued for its ability to grow high-quality diamonds that are chemically and physically identical to natural diamonds. Here’s how the process works:
-
Starting with a Diamond Seed
- The process begins with a thin slice of diamond, known as a “seed.” This seed can either be a small natural diamond or a previously grown lab diamond. The seed is placed inside a specialized vacuum chamber.
-
Introducing Carbon Gases
- A gas mixture, typically methane (CH₄) and hydrogen (H₂), is pumped into the vacuum chamber. These gases are rich in carbon, which is the key element in diamond formation.
-
Plasma Activation
- The gases are then exposed to extreme heat using microwaves, which creates a plasma cloud inside the chamber. This high-energy environment breaks down the carbon molecules in the gases, causing the carbon atoms to separate and fall onto the diamond seed.
-
Diamond Growth
- Over several weeks, carbon atoms accumulate on the diamond seed, layer by layer, in a crystalline structure. This process mimics the natural growth of diamonds, but at a significantly accelerated rate.
-
Polishing and Refining
- Once the diamond has grown to the desired size, it is carefully extracted and cut into its final shape. The diamond undergoes traditional cutting and polishing to enhance its brilliance and luster.
Advantages of CVD Diamonds:
- Lower Temperatures: The CVD process operates at lower temperatures than HPHT, reducing the risk of metal inclusions and allowing for greater control over diamond purity.
- Uniform Growth: CVD allows for more consistent and uniform diamond growth, resulting in high-quality diamonds with fewer inclusions or imperfections.
- Customizable Properties: CVD diamonds can be grown with specific properties, such as color or clarity, by adjusting the gases and conditions in the chamber.
CVD diamond when tested with presidium (diamond tester), it will show ‘Diamond’. This is not true for HPHT diamond.
What is HPHT diamond? Learn more…